
With the explosive growth of data and the need for scalable and efficient systems, traditional relational and NoSQL databases have faced limitations. This has led to the emergence of distributed SQL databases, revolutionizing how organizations handle their data.
Choosing the right database to power modern applications can be challenging. For starters, as data volumes grow when using a traditional relational database, performance and scalability radically degrade. These problems can only be remedied with additional data processing, aggregation, and integration tools. However, such solutions create greater technical complexity for developers, poor real-time performance, and higher data storage costs.
In this blog, we’ll explore what a true distributed SQL database is, why this growing category elevates modern application development, and the advantages it offers over traditional database systems. By the end of this post, you’ll have all the information you need to take the next step in your company’s cloud-native journey.
What is a Distributed SQL Database?
Distributed SQL is a type of database architecture that distributes data across multiple nodes, allowing for elastic scalability, relentless reliability, and faster query processing of mixed workloads. Unlike traditional SQL databases that rely on a single-node server to store and process data, distributed SQL databases distribute data across multiple servers, also known as nodes. Each node operates independently, but also communicates with other nodes to ensure that data is consistent and available for processing.
Distributed SQL databases work by partitioning data into smaller, more manageable subsets, known as shards. Each shard is stored on a separate node, and queries that involve data from multiple shards are executed across multiple nodes simultaneously. This allows for faster query processing and better performance, as each node can process queries in parallel.
Additionally, distributed SQL databases with mixed workload processing capabilities can combine row and column storage in a single database. This provides a single endpoint for mixed workloads while guaranteeing strong data consistency. Data can also be collected from multiple applications and aggregated instantly, allowing real-time queries to be performed on online operational data.
How Does Distributed SQL Architecture Work?
A distributed SQL database architecture is divided into two primary layers: the compute layer and the storage layer:
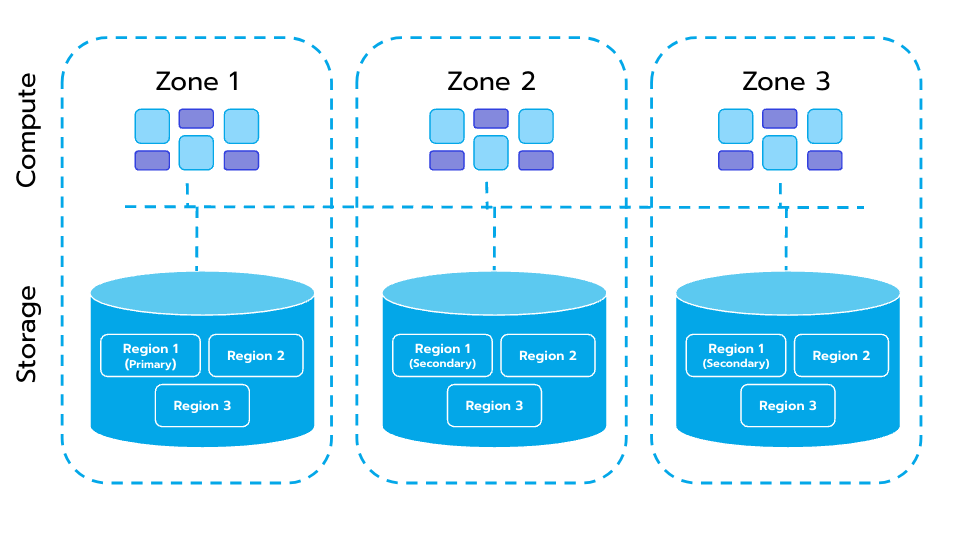
Figure 1. A typical distributed SQL data architecture.
1. Compute Layer
The compute layer is a stateless SQL layer that exposes the connection endpoint of the SQL protocol to the outside. The compute layer receives SQL requests, performs SQL parsing and optimization, and ultimately generates a distributed execution plan. It is horizontally scalable and provides a unified interface to the outside world through load balancing components. This layer is only for SQL computing and analyzing as well as transmitting actual data read requests to the storage layer.
2. Storage Layer
The storage layer is responsible for storing data using a distributed transactional key-value storage engine.
Region is the basic unit to store data. Each Region stores the data for a particular Key Range, which is a left-closed and right-open interval from StartKey to EndKey.
Multiple Regions exist in each storage node. Storage APIs provide native support to distributed transactions at the key-value pair level and support Snapshot Isolation by default. This is the core of how a distributed SQL database supports distributed transactions at the compute layer.
After processing SQL statements, the compute layer converts the SQL execution plan to an actual call to the storage layer API. Therefore, the storage layer stores the data. All storage layer data is automatically maintained in multiple replicas (three replicas by default). These replicas grant the storage layer native high availability and automatic failover capabilities.
What Are the Technical Benefits of Distributed SQL?
Distributed SQL databases offer several technical benefits over traditional SQL databases, including:
- Scalability: As data volumes grow, these databases can easily scale in or out to handle the load, by adding or removing nodes as needed. This makes it possible to handle large-scale data processing and storage without sacrificing performance.
- Fault tolerance: These databases are designed to be fault-tolerant, which means they can continue to operate even if one or more nodes fail. This is achieved by replicating data across multiple nodes, so that if one node fails, data can still be retrieved from other nodes.
- High availability: These databases can provide high availability, ensuring that data is always accessible, even in the event of a node failure. Again, data replication achieves this, which ensures data is always available on multiple nodes.
- Mixed workload processing: These databases can provide efficient complex query processing of mixed workloads, enabling greater developer productivity, a simplified architecture, and real-time data aggregations.
Distributed SQL databases are becoming increasingly popular as organizations look for ways to manage and process large volumes of data efficiently. As data continues to grow at an exponential rate, distributed SQL databases will become even more important for modern application development.
What Are the Business Benefits of Distributed SQL?
Distributed SQL databases power business-critical transactional applications with a SQL-compatible tech stack, extreme elastic scaling, and continuous access to data—all in a single database.
- Accelerate productivity by building new features and apps faster
- Reduce costs by doing more business with less infrastructure
- Lower risk by ensuring continuous access to data anywhere in the world
- Increase innovation by generating real-time operational insights on transactional data
Why Are Distributed SQL Databases an Ideal Solution for Modern Application Development?
In recent years, distributed SQL databases have emerged as a popular relational database alternative. They offer the benefits of traditional SQL and NoSQL databases. They also allow for more efficient data processing of mixed workloads and storage across multiple nodes.
Let’s explore why distributed SQL databases elevate modern application development and the advantages they offer over traditional database systems.
Handling Ever-Increasing Database Requirements
In today’s data-driven world, organizations are generating and collecting vast amounts of data at an unprecedented rate. From user interactions to IoT devices, the volume, velocity, and variety of data are continually expanding.
Figure 2. The acceleration of new customer experiences into digital channels is driving the creation of modern software applications as digital services.
As a result, businesses face the significant challenge of effectively managing and processing this ever-increasing data. Distributed SQL databases have emerged as a robust solution to address these escalating data requirements, and provide the following capabilities:
- Scalable data storage: Instead of relying on a single server, these databases distribute data across multiple nodes in a cluster. As data grows, organizations can seamlessly add new nodes to the cluster, allowing for horizontal scaling.
- Elastic computing power: Distributed SQL databases leverage the distributed nature of their architecture to distribute query execution across multiple nodes. This parallel processing capability enables organizations to leverage the combined computing power of the cluster. This results in faster query response times and improved overall system performance.
- Data compression and optimization: By compressing data, these databases reduce the storage footprint, allowing organizations to store more data within the same infrastructure.
Increasing Modern Application Scalability and Availability
Organizations strive to deliver highly-scalable and always-on applications that provide an exceptional user experience. However, traditional database systems often struggle to keep up with the scalability and availability demands of modern applications, which require real-time responsiveness.
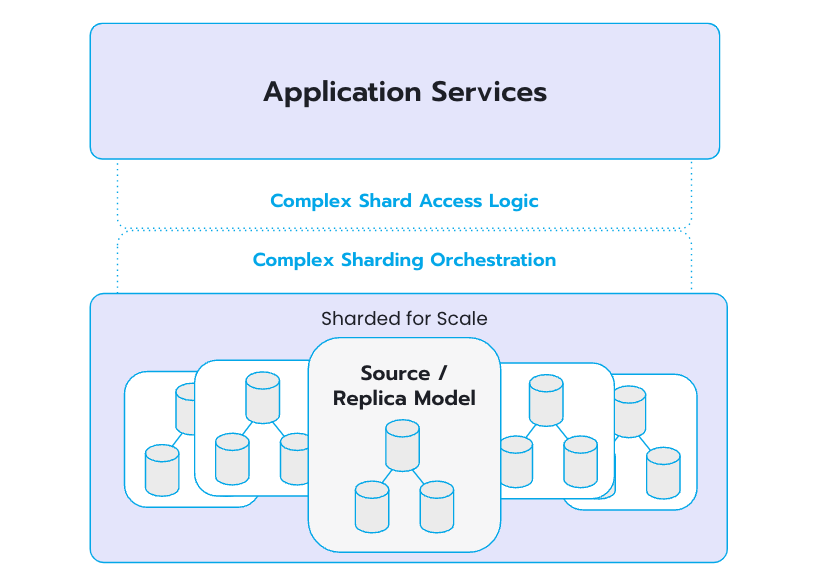
Figure 3. An example of a traditional database system that implements sharding, adding technical complexity.
Distributed SQL databases have emerged as a powerful solution to address these challenges and significantly improve application scalability and availability. Here’s how they do it:
- Distributed query execution: By dividing query workloads across clusters, distributed SQL databases can harness the collective computational power of the nodes. This effectively reduces the response times for complex queries.
- Disaggregated storage and compute architecture: In a disaggregated storage and compute architecture, different functionalities are divided and allocated to two types of nodes: the Write Node and the Compute Node. This means you can decide the number of Write Nodes and Compute Nodes to be deployed as needed.
- Intelligent data placement: Distributed SQL databases can intelligently distribute and replicate data across data nodes in multiple availability zones (AZs), offering high availability and fault tolerance. This means if a single node or less than half of the nodes fail, the system can continue to function, a characteristic traditional monolithic databases can never achieve.
Streamlining the Tech Stack Jungle
In a rapidly-evolving tech landscape, companies often find themselves navigating through a complex jungle of technologies, frameworks, and tools. Managing multiple components and integrating them seamlessly can be a daunting task.
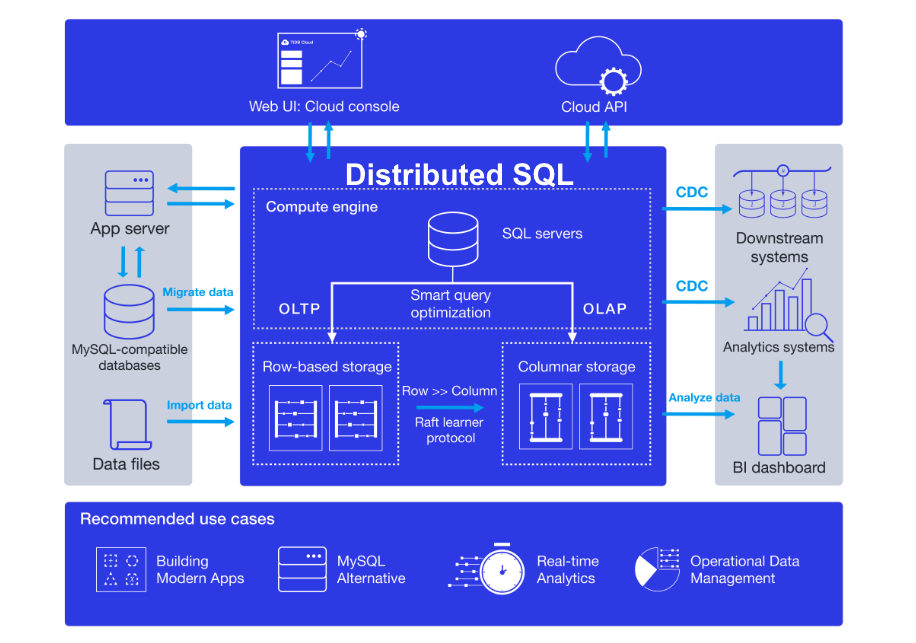
Figure 4. An example of a distributed SQL architecture with scalability and reliability for modern transactional apps coupled with real-time analytics on transactional data.
Distributed SQL databases offer a valuable solution by streamlining the tech stack jungle, simplifying the architecture, and reducing the complexity associated with data management:
- Consolidated data management: Distributed SQL databases consolidate different data management needs into a single, unified system. By consolidating data management, organizations can simplify their tech stack, reduce integration challenges, and streamline their operations.
- Integration with ecosystem tools and frameworks: These databases are designed to seamlessly integrate with popular ecosystem tools and frameworks. They provide connectors and APIs for integration with programming languages, frameworks, and data processing platforms.
- Simplified data operations: Distributed SQL databases provide built-in automation and management tools and utilize automatic rolling upgrades since they upgrade nodes one-by-one, minimizing impact to the running cluster. They also offer intuitive web-based interfaces or command-line tools that provide a unified view and control over the entire distributed database cluster.
How Can You Get Started with Distributed SQL?
Selecting the right distributed SQL database to power modern applications can be challenging. However, there’s a better option that can evolve alongside your organization. Introducing TiDB, one of the most advanced open-source, distributed SQL databases.
TiDB can power all of your modern applications with elastic scaling, real-time analytics, and continuous access to data. Companies using TiDB for their scale-out RDBMS and internet-scale OLTP workloads benefit from a distributed database that is:
- MySQL compatible: Enjoy the most MySQL compatible distributed SQL database on the planet. TiDB is wire compatible with MySQL 5.7. This means developers can continue to enjoy the database’s rich ecosystem of tools and frameworks.
- Horizontally scalable: TiDB grants total transparency into data workloads without manual sharding. The database’s architecture separates compute from storage to instantly scale data workloads out or in as needed.
- Highly available: TiDB guarantees auto-failover and self-healing for continuous access to data during system outages or network failures.
- Strongly consistent: TiDB maintains ACID transactions when distributing data globally.
- Mixed workload capable: A streamlined tech stack makes it easier to produce real-time analytics. TiDB’s Smart Query optimizer chooses the most efficient query execution plan, which consists of a series of operators.
- Hybrid and multi-cloud enabled: With TiDB, IT teams can deploy database clusters anywhere in the world, in public, private, and hybrid cloud environments on VMs, containers, or bare metal.
- Open source: Unlock business innovation with a distributed database that’s 100% open source under an Apache 2.0 license.
- Secure: TiDB protects data with enterprise-grade encryption both in-flight and at-rest.
Want to take a tour through the fundamentals of a modern distributed database? Check out our in-depth eBook to uncover why distributed SQL databases matter, how they’re architected, and how they’re used in real-world production environments.
Experience modern data infrastructure firsthand.
TiDB Cloud Dedicated
A fully-managed cloud DBaaS for predictable workloads
TiDB Cloud Serverless
A fully-managed cloud DBaaS for auto-scaling workloads



