
Comparison
February 27, 2026
SingleStore vs TiDB: A Guide to Choosing the Right Distributed SQL Database

Engineering
February 26, 2026
Solving the Distributed Backup Headache: How TiDB Delivers Transactional Consistency

What Is
February 18, 2026
Raft Region Size: The Invisible Lever for Distributed Database Performance

Thought Leadership
February 17, 2026
The Hidden Cost of Database Over-Provisioning

Tutorial
February 13, 2026
How to Build an AI Advisor That Shows College ROI (Not Rankings)

Community
February 12, 2026
LLM Reasoning vs. Vector Search: Lessons from Building CrowdSnap’s Sentiment Analytics

Community
February 11, 2026
Prompt To Production: Building Scalable AI on TiDB with Kiro
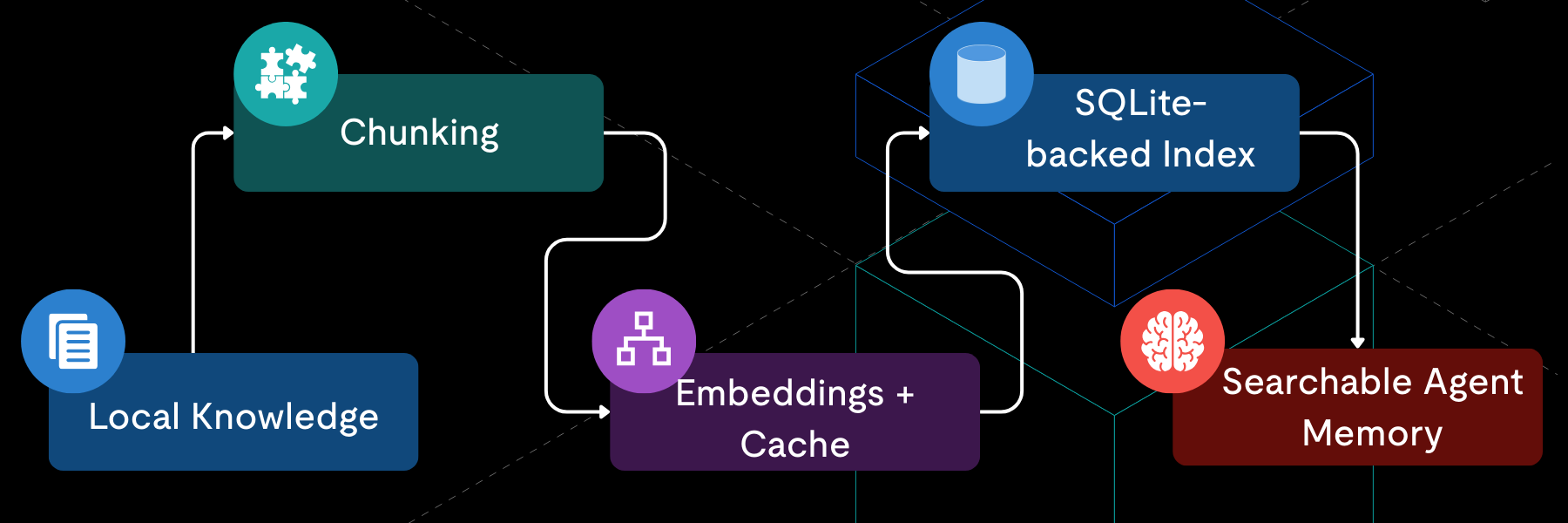
Community
February 6, 2026
OpenClaw Memory Architecture: Building a Local-First RAG with SQLite

Engineering
February 3, 2026
Teaching AI Agents to Speak “Production” SQL: Introducing TiDB Skills

Community
February 2, 2026
The Fire-and-Forget Pattern: Scaling Game Analytics with TiDB Cloud and Convex

Tutorial
January 30, 2026
How to Build a Voice-to-Text App That Learns Your Style (Without Storing Your Words)

Product
January 27, 2026












